Mitigating Human Error in KYC Processes: How Automation Can Enhance Accuracy and Efficiency
Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures are essential in safeguarding financial institutions against fraud, money laundering, and terrorist financing, but they also pose significant challenges due to their complexity and manual nature. Regulatory bodies mandate these processes to ensure that institutions verify their customers’ identities, assess risks, and monitor suspicious activities. However, human error in KYC processes can lead to compliance risks, financial penalties, and operational inefficiencies.
This blog examines how automation technologies can mitigate human error in KYC processes, enhancing accuracy, speed, and regulatory compliance, while addressing the intricacies of implementing automation effectively.
Overview of Human Error in KYC Processes
Human error is a persistent and significant challenge within Know Your Customer (KYC) processes due to their repetitive, data-heavy, and multifaceted nature. Financial institutions require precise data handling, document verification, and accurate customer risk assessments to comply with stringent regulatory standards.
However, the complex steps involved in KYC, compounded by high-volume data entry and continuous decision-making, heightens human error potential.
Below are the most common sources of human error within KYC processes, along with their implications:
1. Data Entry Errors
One of the most pervasive sources of human error in KYC is manual data entry. Employees often need to transcribe information from identification documents, such as passports, driver’s licenses, or national ID cards, into internal systems. Even small typographical errors, such as a misspelled name or incorrect date of birth, can disrupt the KYC process by leading to false customer matches, unnecessary alerts, or even non-compliance. For example, an incorrect birthdate might mismatch a legitimate client with a flagged individual, triggering unnecessary screening and causing delays.
Such errors not only impede process efficiency but also raise regulatory concerns, as financial institutions are mandated to maintain accurate records to mitigate risks associated with identity theft and financial crime.
2. Inconsistencies in Document Handling
KYC processes involve a wide range of documents that vary by country, client type, and institution requirements. Employees must verify government-issued IDs, bank statements, utility bills, and other supporting documents, each of which may present unique formats, security features, and languages.
Human employees often face challenges interpreting these documents consistently, especially when working with unfamiliar or non-standard document formats, documents in foreign languages, or those lacking uniform security elements. Misinterpretations, such as confusing official seals with potential tampering or misidentifying document authenticity features, can lead to erroneous assessments and further complicate compliance efforts.
3. Subjective Decision-Making
Subjective judgment can introduce significant inconsistencies in KYC processes. Each step, from determining customer risk profiles to assessing potential red flags, requires decisions that may vary between employees based on experience, knowledge, and interpretation. These judgments may be inconsistent, especially during high-pressure situations or workload surges, resulting in some customers facing stricter assessments than others.
For instance, one employee might flag a client as high-risk due to an ambiguous transaction, while another may interpret the same transaction as benign. This variability can lead to unpredictable outcomes, potentially affecting customer relationships and undermining the institution’s overall risk management framework.
4. Delayed Processes and Bottlenecks
Manual KYC processes are inherently slower, especially during high-demand periods. Each step, from document collection to data entry, is time-consuming, creating bottlenecks that can impact the onboarding process and compliance timelines.
As backlogs build up, employees may rush through assessments, increasing the likelihood of oversights and skipped steps. Delays can also result in regulatory breaches if institutions fail to meet compliance deadlines for onboarding and periodic KYC reviews, exposing them to penalties and reputational damage. Furthermore, delayed KYC processes frustrate customers, who may abandon the onboarding process altogether, impacting customer acquisition.
5. Challenges in Cross-Referencing Data from Multiple Sources
KYC processes require employees to cross-reference customer information from various sources, such as databases, transaction histories, and government records.
Ensuring that all data points align is crucial, but when done manually, this cross-referencing process is highly susceptible to errors. Employees may miss data discrepancies, overlook potential risk indicators, or misalign information due to variations in data formatting between sources. For example, a slight difference in a customer’s name between two documents could be overlooked, which may result in inaccurate risk assessments or incomplete customer profiles.
Implications of Human Error in KYC Processes
The impact of human error within KYC is far-reaching and can undermine both operational and regulatory objectives. Errors in data entry or document verification can create vulnerabilities in the compliance framework, leading to:
- Increased Compliance Risks: Inaccurate customer data or inconsistent assessments weaken the institution’s ability to monitor and mitigate risk, potentially violating Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF) regulations. Regulatory breaches not only lead to fines but also increased scrutiny, which may impose long-term constraints on operations.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Human errors result in rework, such as additional verification steps, repetitive data checks, and unnecessary alerts, which slow down the process and increase operational costs. Inconsistent or subjective decision-making also demands added layers of review, further straining resources.
- Reputational Damage: Inaccurate or inconsistent customer treatment due to human error can damage customer trust, especially if clients experience delays or are erroneously flagged as high-risk. The reputational impact can lead to reduced customer retention and a loss of market confidence, both of which have long-term financial repercussions.
- Regulatory Penalties: Many regulatory bodies enforce strict penalties for KYC non-compliance, especially in cases where institutions fail to maintain accurate records or promptly flag suspicious activities. Frequent human errors that disrupt these processes expose institutions to substantial fines and legal challenges, eroding stakeholder trust.
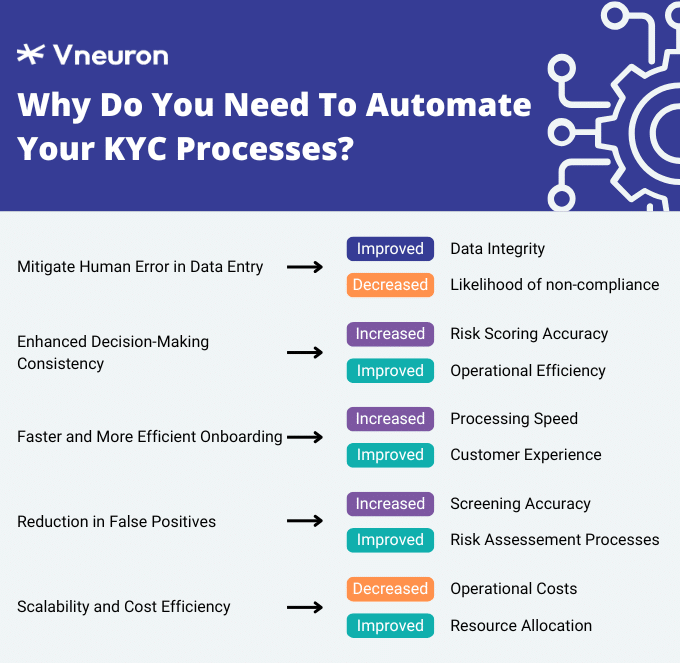
These factors underscore the need for solutions that minimize human involvement in error-prone tasks, allowing institutions to maintain high standards of accuracy and regulatory compliance. Automation offers a robust pathway to mitigate these issues by standardizing and streamlining KYC procedures, thereby reducing error rates and optimizing operational efficiency.
Role of Automation in KYC Processes
Automation enhances KYC processes by improving precision, consistency, and processing speed, effectively reducing the margin for human error. By incorporating advanced technologies, financial institutions can streamline traditionally manual tasks, minimizing the chances for errors and ensuring KYC processes adhere to regulatory standards.
Automation’s impact on KYC is observed primarily through three critical areas:
1. Standardization of Data Entry and Verification
Automated data entry enforces standardized data formats and structures, significantly reducing discrepancies and enhancing data integrity. Unlike manual entries prone to typographical errors or inconsistencies, automated systems can validate and correct data in real-time, minimizing transcription error.
These systems ensure all data entries align with predefined formats, reducing inconsistencies that could otherwise lead to false alerts or customer mismatches. Automated data verification also performs continuous data integrity checks, notifying compliance teams of significant inconsistencies for immediate resolution.
2. Automated Document Verification and Data Extraction
Advanced document verification technologies streamline the verification of various customer documents. Machine learning algorithms trained on thousands of document templates can verify key identification markers, such as document type, issuing authority, and expiration date, reducing human handling errors.
These automated systems can accurately process and verify diverse document types in multiple formats, even in cases with unique security features or foreign jurisdiction standards in real time, enhancing the reliability of document-based KYC.
3. Enhanced Decision-Making via Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning Models
Machine learning models trained on extensive KYC data history create predictive insights that improve decision consistency and accuracy across customer risk assessments. These models help automate risk scoring, relying on rule-based algorithms and predictive analytics to identify high-risk customers with a level of precision that reduces human bias and inconsistency. Predictive analytics technologies have proven to be particularly useful for detecting subtle patterns of suspicious behavior that might otherwise go unnoticed, contributing to a substantial reduction in false positive rates.
Automation not only streamlines KYC by handling repetitive, error-prone tasks but also empowers institutions to scale their compliance efforts more effectively. By integrating automated systems, institutions can focus human resources on higher-value activities such as complex case analysis and strategic decision-making, thereby reinforcing their overall compliance framework.
Enhancing and Automating KYC Processes: The Role of Technology
A sophisticated technology stack drives automation in KYC, allowing each component to address unique aspects of AML compliance while reducing the need for manual intervention.
The following technologies play a pivotal role in enhancing KYC accuracy:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is integral to automating high-volume, rule-based tasks within KYC workflows, enabling institutions to standardize data management processes and handle repetitive tasks without human input. The technical capabilities of RPA in KYC include:
- Data Aggregation and Migration: RPA bots consolidate customer data from multiple internal and external sources, reducing data-handling inconsistencies and potential errors.
- Real-Time Data Validation: RPA bots conduct on-the-fly validation of data, checking fields for completeness, logical consistency, and format adherence. Bots can flag inconsistencies in real time, alerting compliance teams to review data fields that could introduce risk factors.
- Scalability and Rapid Deployment: RPA is highly scalable, allowing institutions to quickly adapt to increasing workloads or regulatory changes by deploying additional bots. This scalability is particularly beneficial for institutions experiencing rapid growth.
RPA simplifies complex workflows by automating routine processes, reducing manual handling errors, and accelerating data processing speed across large KYC volumes.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML offer a higher intelligence layer that optimizes KYC accuracy through adaptive learning models. With machine learning, KYC systems can leverage predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and continuous learning to minimize human error and improve customer assessments.
- Adaptive Risk Scoring Models: ML algorithms generate risk scores by evaluating extensive customer profiles, transaction behaviors, and historical data, standardizing risk assessments. These models evolve with every new data input, continually refining their accuracy and drastically reducing human error.
- Anomaly Detection: By recognizing patterns within customer behavior, ML-based systems can identify deviations that signal potential terrorism financing or money laundering. These models operate on probability metrics, enabling early detection of risky transactions and reducing false negatives.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Information Extraction: NLP, a subset of AI, automates the extraction of relevant data from unstructured text fields such as customer documents.NLP algorithms categorize, interpret, and structure data with a precision that significantly reduces manual extraction errors.
AI and ML enhance KYC processes by proactively identifying risks, improving risk assessment reliability, and ensuring data integrity without the need for extensive human intervention.
Automating Sanctions and PEP Screening In the KYC
Sanctions and Politically Exposed Persons (PEP) screening is essential in identifying high-risk individuals and entities, a fundamental component of comprehensive KYC processes. Automation and AI enhance the accuracy and efficiency of these screenings, reducing false positives and enabling real-time risk mitigation.
- Automated Screening Across Global Sanctions Lists: Automated systems continuously monitor and cross-reference multiple sanctions and PEP lists globally, ensuring complete and up-to-date AML compliance. This process significantly enhances the speed of risk detection and minimizes exposure to non-compliance.
- Fuzzy Matching Algorithms and Dynamic Risk Assessment: Machine learning algorithms use fuzzy matching to account for variations in names or translations across different languages, reducing false positives by approximately 95%. These models can also assess match probability, helping compliance teams focus only on high probability alerts.
- Real-Time Alerting and Intelligent Case Management: Advanced systems generate alerts in real-time upon detecting a potential match, enabling immediate review by compliance teams. Automated case management solutions organize flagged cases based on priority, improving response times and minimizing overlooked risks.
In summary, automated technologies significantly enhance KYC processes by reducing human involvement in error-prone tasks, allowing institutions to operate at scale while maintaining accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Benefits of Automation in KYC Compliance
The deployment of automation in KYC processes offers financial institutions numerous advantages, each contributing to more efficient and compliant KYC workflows.
Increased Efficiency and Faster Processing Times
Automated processes streamline data handling, document verification, and customer authentication, enabling faster onboarding and KYC compliance. RPA bots, for instance, handle data aggregation and validation in seconds, allowing human employees to focus on strategic tasks. By reducing time spent on manual KYC tasks, institutions can onboard customers more swiftly, improving customer satisfaction and expanding their client base.
Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency
Automation minimizes human error by standardizing tasks across KYC workflows. AI and ML algorithms apply uniform rules when assessing customer risk or screening documents, leading to higher accuracy and fewer false positives. This consistency ensures that KYC processes are reliable, even at scale, strengthening institutions’ compliance with regulatory requirements.
Cost Reduction and Improved Resource Allocation
Automated KYC systems reduce the need for manual data entry, verification, and analysis, lowering operational costs over time. Financial institutions can reallocate resources away from repetitive tasks to high-value activities, such as customer engagement or fraud investigation. Automation thus enables institutions to optimize resource utilization while maintaining compliance.
Improved Regulatory Compliance
Automated KYC processes help institutions meet stringent regulatory standards by reducing the risk of compliance errors. Automation tools maintain detailed audit trails, enabling regulators to review each step of the KYC process easily. By keeping processes consistent and well-documented, automation improves the transparency and traceability of KYC operations, bolstering institutions’ compliance capabilities.
As the financial industry continues to navigate complex regulatory requirements and evolving threats, automation in KYC processes is becoming increasingly indispensable. By reducing human error and streamlining operations, automation enables institutions to maintain compliance more efficiently and accurately. As the technology continues to advance, the potential for even greater improvements in accuracy, speed, and security will undoubtedly reshape the future of KYC.
To enhance your KYC processes with cutting-edge automation, explore how Vneuron’s award-winning solution can help you achieve a higher level of compliance and operational excellence.

